已不生产
AT指令
AT+NAME
hc01.comV2.0
AT+NAMEXXXX
OKsetname
AT+PIN1234
receive:OKsetPIN
已不生产
AT指令
AT+NAME
hc01.comV2.0
AT+NAMEXXXX
OKsetname
AT+PIN1234
receive:OKsetPIN
arm64-v8a 存放64位 so
armeabi-v7a 存放32位 so
其他架构目录基本不需要理会
如何让64位应用强制以32位模式启动 并读取对应目录下的 so呢?
app.gradle
android {
defaultConfig {
ndk {
abiFilters "armeabi-v7a"
}
}
}
在defaultConfig 强制配置armeabi-v7a 就会读取对应目录的so
gradle.properties
android.useDeprecatedNDK=true
强制以deprecated模式读取
AT +OK
AT+VERSION 版本信息
AT+NAME 查看蓝牙socket名字
AT+NAMEROBIN 设置蓝牙socket名字为ROBIN
AT+NAMB 查看低功耗蓝牙名字
AT+NAMBROBIN 设置低功耗蓝牙名字为ROBIN
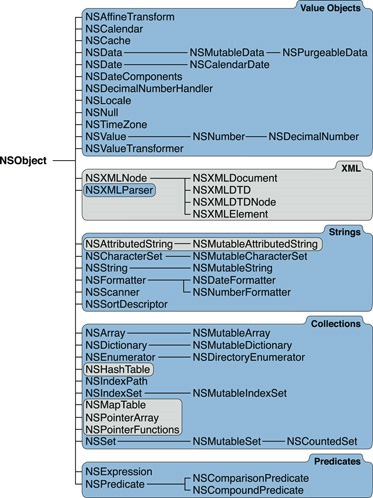


Saler.h //头文件声明声明对外公开的方法 声明公共属性和私有属性
@interface Saler : NSObject {
@private NSThread *thread;
}
@property NSNumber *ticket;
-(void) startSale;
@endSaler.m //声明具体方法实现 init为默认的构造函数
#import "Saler.h"
@implementation Saler
-(Saler*) init{
self = [super init];
NSLog(@"init saler");
self.ticket = [NSNumber numberWithInt:20];
//公共属性用.访问
return self;
}
-(void) startSale{
NSThread *thread = [NSThread new];
self->thread = thread;
//私有属性用->访问
[thread initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(run) object:nil];
[thread start];
}
-(void) run{
NSLog(@"running");
}
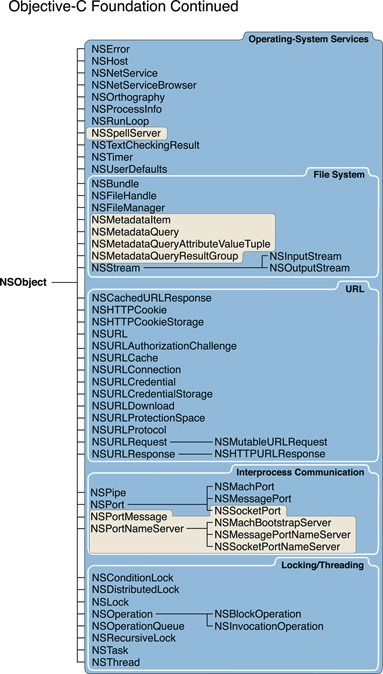
@endNSNetService //socket server
NSPort
子类有NSSocketPort(ip地址 + 端口) //socket client
子类有NSMachPort(应用消息通讯) 多线程通过此端口应用通讯
子类有NSMessagePort (NSMachPort对消息的封装)
但是 objective-c 有
NSConnection
NSURL
用来处理http请求 file请求 ftp请求 都是一些比较上层的应用层协议
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"https://www.baidu.com"];
//2、创建请求(Request)对象(默认为GET请求);
NSURLRequest *requst = [[NSURLRequest alloc]initWithURL:url];
//3、发送请求
/*
第一个参数:请求对象
第二个参数:响应头
第三个参数:错误信息
返回值:NSData类型,响应体信息
*/
NSError *error = nil;
NSURLResponse *response = nil;
//发送同步请求(sendSynchronousRequest)
NSData *data = [NSURLConnection sendSynchronousRequest:requst returningResponse:&response error:&error];
NSLog(@"connection data:%@",[[NSString alloc]initWithData:data encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]);
NSLog(@"connection error:%@",error);sudo killall -STOP -c usbd命令执行后可以正常连接
文件输入流
NSMutableData *data = [NSMutableData new];
NSInputStream *inputStream = [NSInputStream inputStreamWithFileAtPath:@"/Users/dengfang/111.txt"];
[inputStream open];
NSLog(@"数据读取中...");
while(1){
uint8_t buf[1024];
NSInteger readLength = [inputStream read:buf maxLength:1024];
if (readLength > 0) {
[data appendBytes:buf length:readLength];
} else {
NSLog(@"未读取到数据");
break;
}
}
NSLog(@"%@" ,[data base64EncodedStringWithOptions:nil]);
}文件输出流
NSOutputStream *ouputStream = [NSOutputStream outputStreamToFileAtPath:@"/Users/dengfang/222.txt" append:false];
[ouputStream open];
[ouputStream write:data.bytes maxLength:data.length];
[ouputStream close];NSThread 为objective-c 的多线程对象
#import "Saler.h"
@implementation Saler
-(Saler*) init{
self = [super init];
NSLog(@"init saler");
self.ticket = [NSNumber numberWithInt:20];
return self;
}
-(void) startSale{
NSThread *thread = [NSThread new];
self->thread = thread;
[thread initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(run) object:nil];
//该访问指明调用self.run 方法作为线程运行代码
[thread start];
}
-(void) run{
NSLog(@"running");
}
@endmain 函数
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Saler.h"
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
Saler* saler1 = [Saler new];
Saler* saler2 = [Saler new];
[saler1 startSale];
[saler2 startSale];
NSLog(@"starting");
}
return 0;
}
console output
2023-04-02 20:58:33.568419+0800 CMD[2079:186178] init saler
2023-04-02 20:58:33.568662+0800 CMD[2079:186178] init saler
2023-04-02 20:58:33.569828+0800 CMD[2079:186178] starting
2023-04-02 20:58:33.570763+0800 CMD[2079:186233] running
2023-04-02 20:58:33.570776+0800 CMD[2079:186234] running
Program ended with exit code: 0NSDate
NSDate *date = [NSDate new]; //默认为当前日期
//NSDate *date = [NSDate date]; //调用date方法也可以
NSLog(@"print date is %@",date);dateFormat 格式化输出
NSDateFormatter *formatter = [NSDateFormatter new];
formatter.dateFormat = @"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss z";
//[formatter setDateFormat:@"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss z"];
NSString *str = [formatter stringFromDate:date];
NSLog(@"print date is %@",str);dateFormat 反格式化
NSString *dateString = @"2023-04-02 11:33:04";
NSDateFormatter *formatter = [NSDateFormatter new];
[formatter setDateFormat:@"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"];
NSDate *date = [formatter dateFromString:dateString];
NSLog(@"print date is %@",date);