
jenkins 是一个服务端服务持续集成的框架,用于管理项目部署脚本。
最简单的安装方法下载 jenkins war包到本地 通过 java -jar 部署 因其内部自带netty http 服务 用网站进入jenkins 进行项目管理
java -jar jenkins.war --httpPort=8280 在端口8280启动jenkins服务

jenkins 是一个服务端服务持续集成的框架,用于管理项目部署脚本。
最简单的安装方法下载 jenkins war包到本地 通过 java -jar 部署 因其内部自带netty http 服务 用网站进入jenkins 进行项目管理
java -jar jenkins.war --httpPort=8280 在端口8280启动jenkins服务
所有C# 自定义windows form 控件继承自 UserControl 在design中设计界面 在partial class中定义自定义属性和行为
注解解析
[Category("Text"),
Browsable(true),
DefaultValue(typeof(Image), null),
Description("图标")]
public Image Icon { get; set; }
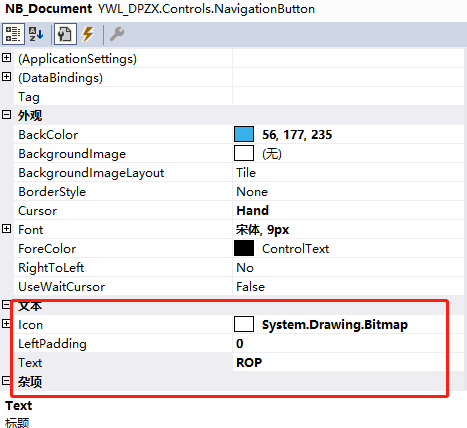
Category 对应分类
Browsable 对应是否能看到
然后还有默认值和描述
这个注解使代码和 设计界面能连通
组件生命周期
form 打开:
• Control.HandleCreated
• Control.BindingContextChanged
• Form.Load
• Control.VisibleChanged
• Form.Activated
• Form.Shown
from 关闭:
• Form.Closing
• Form.FormClosing
• Form.Closed
• Form.FormClosed
• Form.Deactivate
control ,change focus:(使用 tab ,shift + tab等等,或是调用Select,SelectNextControl,或是使用当前form的ActiveControl)
• Enter
• GotFocus
• Leave
• Validating
• Validated
• LostFocus
control ,change focus:(使用鼠标,或是通过调用Focus方法)
• Enter
• GotFocus
• LostFocus
• Leave
• Validating
• Validated
特别是load 事件 可以再InitializeComponent 绑定加载事件 然后 添加渲染后回调操作
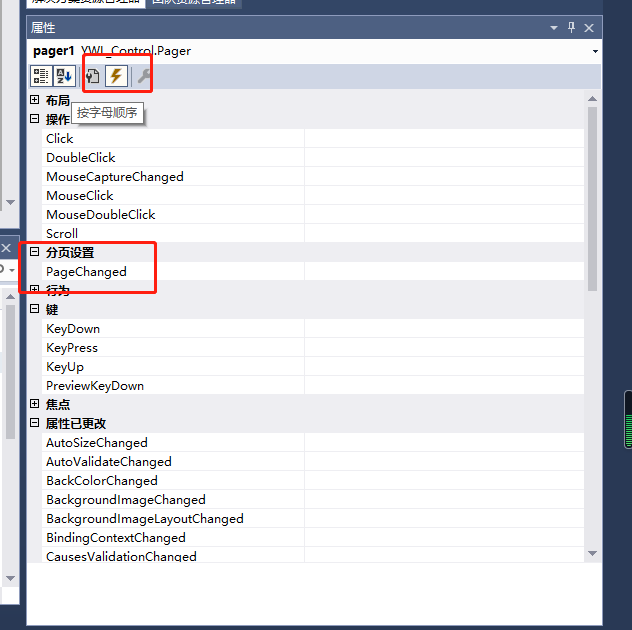
添加自定义事件
public delegate void PageChangeDelegate();//
/// <summary>
/// 当前页改变时发生的事件
/// </summary>
[Description("当前页改变时发生的事件"), Category("分页设置")]
public event PageChangeDelegate PageChanged;在具体的业务流程中调用
private void btnFirst_LinkClicked(object sender, LinkLabelLinkClickedEventArgs e)
{
//设置当前页
CurrentPage = 1;
//设置上一页、下一页是否可用以及当前页按钮字体颜色
SetBtnPrePageAndBtnNextPage();
//调用注册事件
if (PageChanged != null) PageChanged();
}
应用程序安装Newtonsoft.Json
序列化
JsonConvert.SerializeObject(o);反序列化
JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<T>(jsonstr) ;T为指定的泛型
反序列化为JObject
JObject.Parse(jsonstr)C# 可以用dynamic作为动态类型的声明 然后程序可以访问其动态属性
dynamic keyAndValue = new T();
Console.WriteLine(keyAndValue.key)其中key为动态属性 程序不知道keyAndValue对象是否有key属性
泛型类
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace GenericApplication
{
public class MyGenericArray<T>
{
private T[] array;
public MyGenericArray(int size)
{
array = new T[size + 1];
}
public T getItem(int index)
{
return array[index];
}
public void setItem(int index, T value)
{
array[index] = value;
}
}
class Tester
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 声明一个整型数组
MyGenericArray<int> intArray = new MyGenericArray<int>(5);
// 设置值
for (int c = 0; c < 5; c++)
{
intArray.setItem(c, c*5);
}
// 获取值
for (int c = 0; c < 5; c++)
{
Console.Write(intArray.getItem(c) + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
// 声明一个字符数组
MyGenericArray<char> charArray = new MyGenericArray<char>(5);
// 设置值
for (int c = 0; c < 5; c++)
{
charArray.setItem(c, (char)(c+97));
}
// 获取值
for (int c = 0; c < 5; c++)
{
Console.Write(charArray.getItem(c) + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}泛型方法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace GenericMethodAppl
{
class Program
{
static void Swap<T>(ref T lhs, ref T rhs)
{
T temp;
temp = lhs;
lhs = rhs;
rhs = temp;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a, b;
char c, d;
a = 10;
b = 20;
c = 'I';
d = 'V';
// 在交换之前显示值
Console.WriteLine("Int values before calling swap:");
Console.WriteLine("a = {0}, b = {1}", a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Char values before calling swap:");
Console.WriteLine("c = {0}, d = {1}", c, d);
// 调用 swap
Swap<int>(ref a, ref b);
Swap<char>(ref c, ref d);
// 在交换之后显示值
Console.WriteLine("Int values after calling swap:");
Console.WriteLine("a = {0}, b = {1}", a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Char values after calling swap:");
Console.WriteLine("c = {0}, d = {1}", c, d);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
namespace WindowsFormsApplication1
{
public partial class Form2 : Form
{
public Form2()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
Test test;
private void Form2_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
test=new Test();
label1.DataBindings.Add("Text", test, "Str");
label2.DataBindings.Add("Text", test, "Str");
label3.DataBindings.Add("Text", test, "Str");
}
private void textBox1_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
test.Str = textBox1.Text;
}
}
//要使用绑定数据功能,需要模型支持INotifyPropertyChanged接口
public class Test : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
string _str;
public string Str
{
get
{
return _str;
}
set
{
_str = value;
FireStrChanged();
}
}
//必须实现INotifyPropertyChanged接口的此事件
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
//要在.net4.0使用CallerMemberName特性,需要加上后面一段代码
public void FireStrChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName="")
{
PropertyChanged.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
}
namespace System.Runtime.CompilerServices
{
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Parameter, Inherited = false)]
public class CallerMemberNameAttribute : Attribute
{
}
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Parameter, Inherited = false)]
public class CallerFilePathAttribute : Attribute
{
}
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Parameter, Inherited = false)]
public class CallerLineNumberAttribute : Attribute
{
}
}
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「naruto2017」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/szy759590387/article/details/89516163 protected function form()
{
$form = new Form(new InfusionTicket());
$form->select('clinic_id', "诊所信息")->options(Clinic::all()->pluck('name', 'id'))->required();
$form->date('date', __('Date'))->default(date('Y-m-d'))->required();
$form->select('inject', __('Inject'))->options(['静脉输液'=>'静脉输液',"肌肉(皮下)注射"=>"肌肉(皮下)注射","抽血"=>"抽血"])->required();
$form->number('ticket', __('Ticket'))->required();
$form->select('time_index', __('时间'))->options(InfusionTicketController::$timeArray)->required();
$form->hidden('time');
$form->saving(function ($form){
$timeIndex = $form->time_index;
Log::debug('数据');
Log::debug($timeIndex);
$time = InfusionTicketController::$timeArray[$timeIndex];
Log::debug($time);
$form->time= $time;
});
//保存后回调
$form->saved(function ($form){
Log::debug("执行创建");
$model = $form->model();
$clinicId = $model->clinic_id;
$inject = $model->inject=='静脉输液'?'jmsy':'default';
$date = $model->date;
$dateFormat = Carbon::parse($date)->format('Y-m-d');
$timeIndex = $model->time_index;
$ticket = $model->ticket;
Redis::select(2);
$key = 'infusion-tickets:'.$clinicId.':'.$inject.':'.$dateFormat.':'.$timeIndex;
Log::info($key);
Redis::set($key,$ticket);
});
return $form;
在form表单中设置time为不可见(一定要设置time 不然无法保存time信息)
上述代码在保存时 添加time信息
在保存后 把对应信息 存储在redis中
protected function detail($id)
{
$show = new Show(InfusionTicket::findOrFail($id));
$show->panel()->tools(function ( \Encore\Admin\Show\Tools $tools) {
$tools->disableEdit();
});
$show->clinic('诊所信息', function ($clinic) {
$clinic->setResource('/admin/clinics/');
$clinic->field('name',__('Name'));
});
$show->field('date', __('Date'));
$show->field('inject', __('Inject'));
$show->field('ticket', __('Ticket'));
$show->field('time', __('Time'));
return $show;
}详情页面 屏蔽“编辑”按钮
public static function boot()
{
parent::boot(); // TODO: Change the autogenerated stub
static:: deleted(function (InfusionTicket $model) {
Log::debug("模型删除");
$clinicId = $model->clinic_id;
$inject = $model->inject=='静脉输液'?'jmsy':'default';
$date = $model->date;
$dateFormat = Carbon::parse($date)->format('Y-m-d');
$timeIndex = $model->time_index;
Redis::select(2);
$key = 'infusion-tickets:'.$clinicId.':'.$inject.':'.$dateFormat.':'.$timeIndex;
Log::info($key);
Redis::del($key);
});
}在数据模型中 增加删除回调 删除redis值

C#是微软公司发布的一种由C和C++衍生出来的面向对象的编程语言、运行于.NET Framework和.NET Core(完全开源,跨平台)之上的高级程序设计语言。并定于在微软职业开发者论坛(PDC)上登台亮相。
C#是微软公司研究员Anders Hejlsberg的最新成果。C#看起来与Java有着惊人的相似;它包括了诸如单一继承、接口、与Java几乎同样的语法和编译成中间代码再运行的过程。但是C#与Java有着明显的不同,它借鉴了Delphi的一个特点,与COM(组件对象模型)是直接集成的,而且它是微软公司 .NET windows网络框架的主角。
C#是由C和C++衍生出来的一种安全的、稳定的、简单的、优雅的面向对象编程语言。它在继承C和C++强大功能的同时去掉了一些它们的复杂特性(例如没有宏以及不允许多重继承)。C#综合了VB简单的可视化操作和C++的高运行效率,以其强大的操作能力、优雅的语法风格、创新的语言特性和便捷的面向组件编程的支持成为.NET开发的首选语言。
C#是面向对象的编程语言。它使得程序员可以快速地编写各种基于MICROSOFT .NET平台的应用程序,MICROSOFT .NET提供了一系列的工具和服务来最大程度地开发利用计算与通讯领域。C#使得C++程序员可以高效的开发程序,且因可调用由 C/C++ 编写的本机原生函数,而绝不损失C/C++原有的强大的功能。因为这种继承关系,C#与C/C++具有极大的相似性,熟悉类似语言的开发者可以很快的转向C#
国内的可集群 任务调度
程序内部分为两部分
admin 管理控制台
executor 调度执行器
通过管理控制台 向系统提交任务 和绑定到对应的执行器
执行器在安排的时间内执行任务
windows 下可以通过 sc 命令添加服务
sc create gogs start= auto binPath= ""C:\gogs\gogs.exe" web --config "C:\gogs\conf\app.ini""sc create nginx start= auto binPath= ""C:\nginx\nginx.exe" -p "C:\nginx"" DisplayName= nginx-server