amd64 拉取 sonatype/nexus
arm64 拉取 klo2k/nexus3
镜像默认开放8081 挂载目录/nexus-data
默认 admin密码 在容器内部 cat nexus-data/admin.password
amd64 拉取 sonatype/nexus
arm64 拉取 klo2k/nexus3
镜像默认开放8081 挂载目录/nexus-data
默认 admin密码 在容器内部 cat nexus-data/admin.password

K3S token
NAME:
k3s token - Manage bootstrap tokens
USAGE:
k3s token command [command options] [arguments...]
COMMANDS:
create Create bootstrap tokens on the server
delete Delete bootstrap tokens on the server
generate Generate and print a bootstrap token, but do not create it on the server
list List bootstrap tokens on the server
OPTIONS:
--help, -h show helpopkg 是 openwrt 的包管理系统 对标与 APT 在ubuntu\debian
opkg 配置文件 /etc/opkg.conf
查看log sudo k3s kubectl logs -f -n kubernetes-dashboard kubernetes-dashboard-758765f476-x8rc7 应用 yaml sudo k3s kubectl apply -f XXX.yaml 查看所有资源 sudo k3s kubectl get all --all-name-spaces 删除命名空间 sudo k3s kubectl delete ns XXXXX 进入容器命令行 sudo k3s kubectl exec -it nexus-deployment-87b59d446-ht7p4 -n nexus - /bin/bash 创建命名空间 sudo k3s kubectl create namespace logging
列出镜像 sudo k3s ctr i list
删除本地镜像 sudo k3s ctr i rm registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/robinluo/robinluo:v2.0.4
拉取镜像 sudo k3s ctr i pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/robinluo/robinluo:v2.0.4 –plain-http
–plain-http 可指定使用 http拉取镜像
ctr -n k8s.io images pull –platform linux/amd64 my-image:my-tag
镜像打tag sudo k3s ctr i tag registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/robinluo/robinluo:v2.0.4 new tag
导入docker 导出的镜像 ctr i import image.tar
设置mirror
/etc/rancher/k3s/registries.yaml
mirrors:
"docker.io":
endpoint:
- "https://registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com"
mirrors:
"my-registry.com":
endpoint:
- "https://my-registry.com"
configs:
"my-registry.com":
auth:
username: user
password: password另一种设置containerd mirror方法
K3s 将会在/var/lib/rancher/k3s/agent/etc/containerd/config.toml中为 containerd 生成 config.toml。[ 建议不要直接对 containerd 的配置文件进行修改,格式十分的严格 ]
如果要对这个文件进行高级设置,你可以在同一目录中创建另一个名为 config.toml.tmpl 的文件,此文件将会代替默认设置。
config.toml.tmpl将被视为 Go 模板文件,并且config.Node结构被传递给模板。此模板示例介绍了如何使用结构来自定义配置文件
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.mirrors]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.mirrors."docker.io"]
endpoint = ["https://------.mirror.aliyuncs.com", "https://registry-1.docker.io"]
补充ctr 命令分为 i image 镜像 c container 容器 t task 任务(进程)
我们可以分别用 task 命令和 container 命令取停止和启动一个容器实例
containerd 是K3S 默认的容器管理工具 类似于docker
日志路径在 /var/lib/rancher/k3s/agent/containerd/containerd.log
像差是两个图像(两个波面) 对应点的 光程差
其实就是物理意义上的距离
微透镜阵列形成的 光斑 彼此点要相对应 此z方向是一致的 所以计算像差 只需要计算 x 方向 与 y 方向
w(x,y)/delta x = x方向差值/焦距
w(x,y)/delta y = y方向差值/焦距
从而 反推w(x,y) 计算该点的像差
所有点的像差累加(积分) 就是该波面的波前像差
zernike 输入各对应点 对应的差值 就可以计算出像差
泽尼克多项式是一个正交多项式,分为奇偶两类。
奇多项式:

偶多项式:
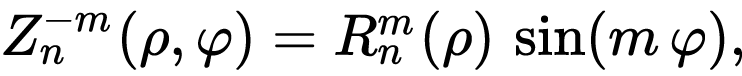
其中:
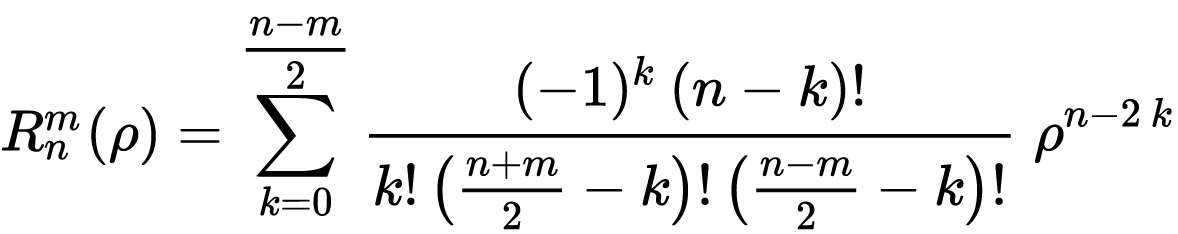
这里fai为方位角,范围[0-2pi];p为径向距离,范围[0,1];n-m大于等于0;
如果n-m=0,则R=0。
根据不同的m和n值,可以得到不同的多项式,用j表示不同的多项式,通常称为Noll序列:
| n,m | 0,0 | 1,1 | 1,−1 | 2,0 | 2,−2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| j | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| n,m | 2,2 | 3,−1 | 3,1 | 3,−3 | 3,3 |
| j | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| n,m | 4,0 | 4,2 | 4,−2 | 4,4 | 4,−4 |
| j | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| n,m | 5,1 | 5,−1 | 5,3 | 5,−3 | 5,5 |
| j | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
jtonmtable 对应的就是这个序列
n m
1 0 0
2 1 1
3 1 -1
4 2 0
5 2 -2
6 2 2
7 3 -1
8 3 1
9 3 -3
10 3 3
11 4 0
12 4 2
13 4 -2
14 4 4
15 4 -4
azimtable 对应的就是 cos sin 角度的系数
cos sin
1 0 0
2 1 0
3 0 1
4 0 0
5 0 2
6 2 0
7 0 1
8 1 0
9 0 3
10 3 0
11 0 0
12 2 0
13 0 2
14 4 0
15 0 4
radialtable 对应的包括 根号系数了
Noll序列前15项泽尼克多项式为:
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2ρcosθ |
| 3 | 2ρsinθ |
| 4 | √3(2ρ2−1) |
| 5 | √6ρ2sin2θ |
| 6 | √6ρ2cos2θ |
| 7 | √3(3ρ3−2ρ)sinθ |
| 8 | √3(3ρ3−2ρ)cosθ |
| 9 | √8ρ3sin3θ |
| 10 | √8ρ3cos3θ |
| 11 | √5(6ρ4−6ρ2+1) |
| 12 | √10(4ρ4−3ρ2)cos2θ |
| 13 | √10(4ρ4−3ρ2)sin2θ |
| 14 | √10ρ4cos4θ |
| 15 | √10ρ4sin4θ |
%% 等待
input('按下回车键继续...');
pause(inf)
需要0度数图片做校准图片(已完成)
相片参数 640×480 = 307200
代码参数 640×520 = 332800 (reconstruction 通过上下加20px 实现)
iv0 = shstruct.ord_sqgrid
dv1 = shstruct.ord_centres
dv2 = shstruct.E1
77 = shstruct.nspots
倩姨打算做一个仿yoto的产品
插卡后 自动播放音频 读取卡片 用条形码 二维码 RFID等方式
安卓做一个原型
APP流程为 手机读取RFID
播放一段音频(可云端 可本地)
原型 solution
用小章鱼作为底 先加入RFID读取功能
再用原生media player 或者 科大讯飞 语音 播放 一段文字